Your skin feels like sandpaper, static shocks greet you at every doorknob, and your hardwood floors are developing suspicious cracks between planks. Welcome to winter’s dry air invasion. A humidifier can transform these arid conditions into comfortable living spaces, but understanding exactly how does a humidifier work helps you choose the right type and use it effectively. This guide breaks down the science behind humidity control, explains each humidifier type’s unique mechanisms, and provides practical usage tips to optimize your indoor environment.
Water Reservoir to Moist Air: The 3-Step Humidification Process
Every humidifier performs three non-negotiable operations regardless of type. First, water storage happens in a dedicated reservoir that feeds the system. Second, vapor generation converts liquid water into breathable vapor using mechanical force, ultrasonic vibrations, or thermal energy. Finally, moisture distribution releases this vapor into your air, raising relative humidity levels to combat desert-like conditions.
This process directly counters winter’s humidity crisis: When cold outdoor air enters your home and gets heated, its moisture capacity expands while actual water content stays fixed. The result? Indoor humidity that often plummets below 15%—drier than Arizona’s Sonoran Desert. By understanding this core sequence, you’ll troubleshoot issues faster and maximize your unit’s efficiency.
Decoding Humidity Science for Practical Use
Why Your Thermostat Lies About Comfort Levels
Relative humidity measures current moisture against maximum possible moisture at a given temperature. This percentage allows meaningful comparison between rooms at different temperatures. Optimal indoor range sits firmly at 30-50% relative humidity per EPA guidelines—anything below causes dry skin and respiratory irritation, while above 60% invites mold growth.
The Cold Air Heating Trap You Can’t Ignore
Cold air holds dramatically less water vapor than warm air. When your heating system pulls in 20°F outdoor air containing minimal moisture and warms it to 70°F, the relative humidity plummets. The warmer air’s expanded moisture capacity makes the actual water content seem even smaller by comparison. This explains why your home feels like a Sahara dune in January despite no actual moisture loss.
How Your Home’s Age Affects Humidity Retention
Well-insulated newer homes better maintain humidity levels while reducing energy consumption. Older houses with drafty windows and porous materials lose moisture faster, requiring more humidification. If your 1920s bungalow needs constant refills while your neighbor’s modern build stays comfortable, construction quality is likely the culprit—not your humidifier.
Whole-House vs. Portable Systems: Mechanism Breakdown

Whole-House Humidifier Operations
Fan-Powered Systems Deliver Round-the-Clock Relief
These units use an independent fan to distribute moisturized air through existing ductwork. They operate even when your furnace is idle, providing consistent humidity control. Higher output capacity makes them ideal for medium to large homes, especially in dry climates where bypass systems can’t keep up.
Bypass Systems Leverage Your Existing HVAC
Bypass humidifiers use your HVAC system’s blower to push air through the unit, requiring additional ductwork for air recirculation. They only function during furnace operation but run whisper-quiet—perfect for smaller homes where noise matters. Critical limitation: They can’t humidify when heating isn’t active.
Steam Systems Conquer Extreme Dryness
Heating elements boil water in a sealed canister, creating pure steam distributed through ducts or a fan pack. These deliver up to double the humidity output of fan-powered systems, making them essential for large homes or arid regions. While energy-intensive, they’re the only option for boiler-heated homes without ductwork.
Portable Humidifier Technologies Explained
Evaporative Cool Mist Units: The Silent Workhorse
A fan draws air through a moist wick filter, causing water to evaporate into vapor. No heat required means quiet operation and child/pet safety. Pro tip: Replace wicks monthly in hard water areas—mineral buildup cripples efficiency. These affordable units excel in single rooms but struggle in very dry climates.
Ultrasonic Models: Zero-Noise Operation
A metal diaphragm vibrates at ultrasonic frequencies (typically 1.7 million times/second), shattering water into microscopic droplets. The result? Completely silent cool mist that evaporates instantly. Warning: Tap water creates visible “white dust” from minerals—use distilled water for clean operation.
Impeller Humidifiers: Kid-Safe Mist Control
Rapidly rotating discs spin water against a diffuser, breaking it into fine droplets. Variable disc speeds let you adjust mist intensity for changing needs. The cool mist output makes it safe around children, though mineral buildup requires weekly vinegar soaks.
Warm Mist Units: Natural Sanitization
Electric heating elements boil water to create pure steam. As the system senses humidity drops, it activates to release sanitized vapor. While effective against airborne pathogens, never place near children—surface temperatures exceed 200°F. Best for bedrooms during cold season.
Critical Usage Guidelines You’re Probably Ignoring
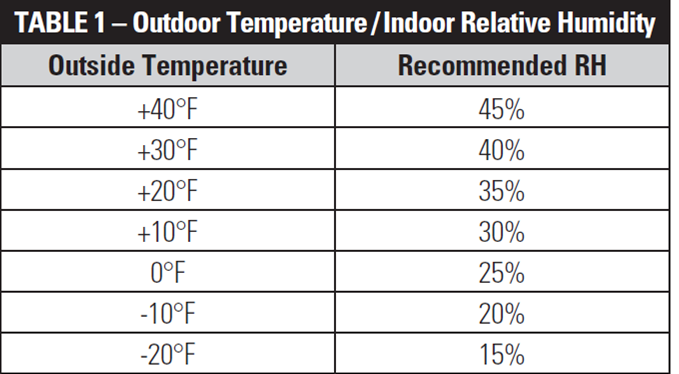
Why Your Humidifier Size Determines Success
Calculate your target space’s cubic footage (length × width × ceiling height). Then factor in home age: Newer, tight-sealed homes retain humidity better, while drafty older houses need 20-30% higher capacity. An undersized unit in a 1,500 sq ft home with 9-foot ceilings will run constantly yet fail to reach 40% humidity.
When to Activate Humidification Immediately
Stop using your humidifier if you see window condensation—this signals dangerous over-humidification. Instead, activate when you experience: persistent dry skin despite moisturizing, static shocks when touching doorknobs, wood furniture developing hairline cracks, or frequent bloody noses indoors. These indicate humidity has dropped below 30%.
The 30-50% Humidity Sweet Spot
Set your humidistat to maintain 30-50% relative humidity. Crucial insight: Built-in hygrometers read 5-10% higher near the device—always verify with a separate hygrometer placed 6 feet away. During extreme cold snaps, temporarily lower settings to 25% to prevent window condensation.
Measurable Benefits Beyond Comfort
Health Improvements Backed by Science
Proper humidification reduces sore throats and sinus irritation by maintaining moist respiratory membranes. Your skin stays hydrated instead of becoming sandpaper-dry. Most significantly, nasal membranes resist cracking that causes bloody noses. Research confirms lower asthma and bronchitis incidence in homes maintaining 40% humidity.
Home Preservation You Can See
Higher humidity makes air feel 3-5°F warmer, potentially reducing heating costs by lowering thermostat settings. Wood floors and furniture resist cracking, while paint and wallpaper maintain integrity. Most noticeably, static electricity shocks become rare—saving you from painful zaps when touching light switches.
Maintenance Mistakes That Kill Humidifiers
The 5-Step Cleaning Protocol That Prevents Mold
Clean after storage periods and monthly during heavy use:
1. Unplug and empty reservoir completely
2. Disassemble all removable parts (filters, tanks, mist nozzles)
3. Soak mineral deposits in 1:1 white vinegar solution for 30 minutes
4. Treat stubborn mold with diluted bleach solution (1 tsp bleach per gallon water)
5. Rinse all parts thoroughly before reassembly
Never skip step 5—bleach residue creates toxic vapors when heated.
Mineral Buildup: The Silent Killer
Tap water minerals create crusty white deposits on fan blades and heating elements, reducing output by 50% within weeks. Proven solution: Use distilled water exclusively in ultrasonic and impeller models. For evaporative units, replace wicks every 1-2 months in hard water areas.
Bacterial Prevention Tactics That Work
Change water daily—even warm mist units harbor bacteria if left stagnant for 48+ hours. Empty tanks when not in use for more than 24 hours. While warm mist units sanitize via boiling, cool mist models require weekly deep cleaning. Critical: Never add essential oils to ultrasonic humidifiers—they damage internal components.
Energy and Water Management Hacks
Energy Star models use 30% less electricity than standard units. Auto-shutoff features prevent waste when tanks empty—expect daily refills for continuous operation. Hard water users should consider whole-house filters to extend component life. Larger tanks (over 1 gallon) cut refill frequency by 50%, ideal for overnight use.
Understanding how does a humidifier work transforms it from a mysterious appliance into a precise humidity control tool. By matching the mechanism to your home’s needs—whole-house systems for tight modern builds or portable units for targeted relief—you’ll maintain that critical 30-50% humidity sweet spot. Remember: Consistent maintenance prevents 90% of failures, with weekly vinegar soaks and distilled water being your simplest defenses against mineral buildup. When winter’s dry air returns, you’ll finally conquer static shocks, cracked wood, and irritated sinuses—not by guessing, but by leveraging the science of moisture control. For ongoing success, pair your humidifier with a $10 hygrometer to verify room-wide humidity levels beyond the unit’s immediate vicinity.





